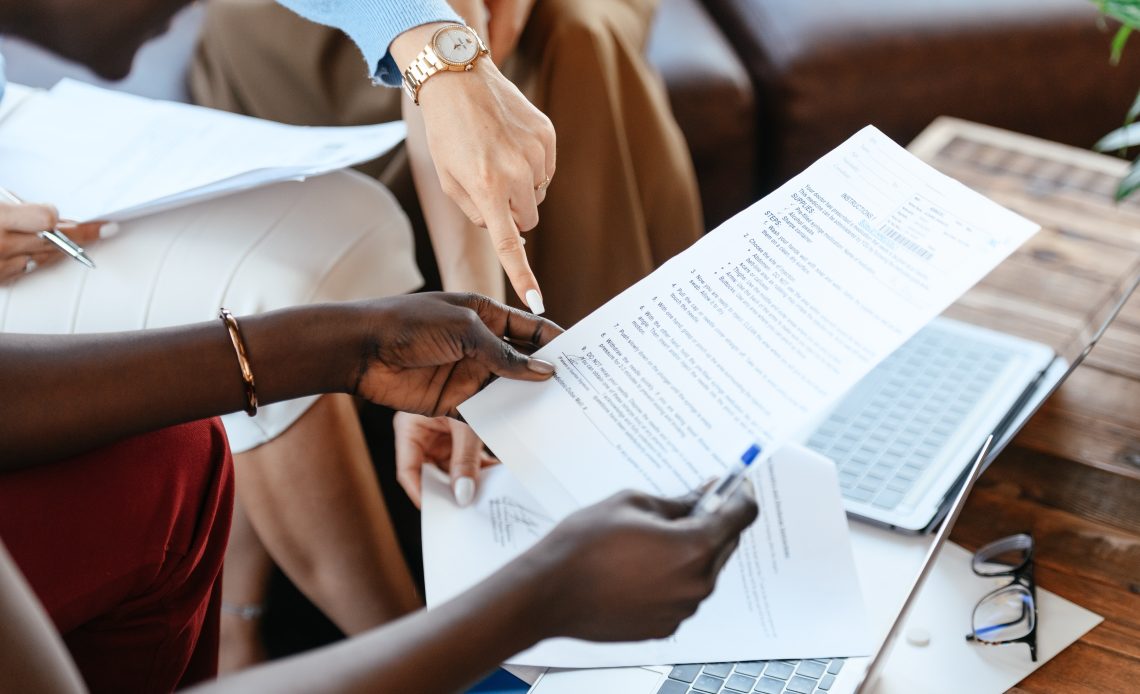
Secondary data refers to data collected by someone other than the researcher. Initially gathered for different purposes, this data type is invaluable, offering insights that can significantly aid new research. Examples include census data, surveys, and organizational records.
Table of Contents
2. Duality of Qualitative and Quantitative Data
Qualitative Secondary Data
- Nature: Explores underlying reasons and motivations.
- Application: Ideal for gaining insights into trends, patterns, and themes.
- Example: Analyzing online reviews to understand customer sentiments.
Quantitative Secondary Data
- Nature: Focuses on numbers and statistical analysis.
- Application: Suitable for making generalizations and identifying correlations.
- Example: Utilizing sales data to forecast future trends.
Learn more: Quantitative vs Qualitative Data: What’s the Difference?
3. The Integral Role of Remote Data Analysts
Remote Data Analysts are at the forefront of interpreting secondary data, turning it into actionable insights by identifying patterns and relationships through advanced statistical tools. They operate across various sectors, ensuring data-driven decision-making.
4. Salary and Qualification Comparison for Remote Data Analysts
| Country | Average Salary (USD) | Qualifications Required | Key Skills |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 75,000 | Bachelor’s degree in a related field; proficiency in R or Python | Statistical Analysis, Data Visualization |
| UK | 50,000 | Bachelor’s degree; proficiency in statistical tools and software | Critical Thinking, Communication Skills |
| Australia | 65,000 | Bachelor’s in a related field; strong analytical skills | Problem Solving, Attention to Detail |
| Canada | 60,000 | Degree in relevant field; experience with data analysis tools | Technical Proficiency, Industry Knowledge |
5. Accessing Free Learning Resources
For those seeking foundational knowledge, platforms like Coursera offer free statistics, programming, and data analysis courses, allowing learners to start their journey into data analytics without any financial investment.
6. Enrolling in the Best Data Analytics Certification Programs
Pursuing certifications from reputed platforms like edX can significantly bolster your resume, offering specialized knowledge and practical skills required for advanced roles in data analytics.

7. Diverse Applications of Secondary Data
Secondary data is a versatile tool, aiding various fields such as:
- Marketing: Identifying consumer behavior and market trends.
- Healthcare: Analyzing patient records for improved healthcare delivery.
- Finance: Forecasting economic trends and investment opportunities.
- Academia: Facilitating in-depth academic research and study.
8. Identifying Examples of Secondary Sources
Understanding what constitutes a secondary source is fundamental in secondary data analysis. A secondary source is a document or recording that relates or discusses information originally presented elsewhere. A quintessential example of a secondary source is a book review. The book contains original content and ideas is a primary source, while the review, which interprets and analyzes the book’s content, is a secondary source. Other examples include:
- Academic Journals: Articles in academic journals typically analyze or review research conducted by others, making them secondary sources.
- Biographies: A biography which interprets and synthesizes life events, is a secondary source.
- Encyclopedias and Textbooks: These resources compile and summarize knowledge from various primary sources, classifying them as secondary.
- Documentaries: Documentaries that analyze and interpret historical events, artefacts, or interviews are secondary sources.
Recognizing secondary sources, such as the examples mentioned above, is crucial for researchers and analysts, as it aids in collecting and interpreting secondary data for further study and analysis.

Conclusion: Mastering Secondary Data Analysis
Secondary data, with its diverse applications and availability, is a cornerstone of research. Mastering its analysis can open doors to various opportunities, whether you aspire to become a Remote Data Analyst or seek to enroll in the Best Data Analytics Certification Programs.
FAQ’s
What is secondary data and examples?
Secondary data refers to information collected by someone other than the user. Common examples include government census reports, weather reports, research studies published in academic journals, and data collected by a business in the past.
What is the meaning of a secondary data set?
A secondary data set refers to a collection of data that was gathered by a different researcher or for another purpose. It’s not collected first-hand by the researcher but is instead derived from already existing sources.
What is secondary data and why is it used?
Secondary data is information previously collected by others that may be used by a researcher for a different purpose. It’s utilized for its time efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and broader scope, allowing researchers to gain insights without conducting a new study.
What is secondary data collection?
Secondary data collection involves gathering existing data that were collected by someone else or for a purpose other than the current research project. This can include both internal data (within the organization) and external data (government publications, online databases).
What are 4 examples of secondary?
Four examples of secondary sources include academic journal articles, biographies, textbooks, and documentaries. These sources analyze, interpret, or summarize information originally presented elsewhere.
What is primary data vs secondary data?
Primary data is data collected firsthand by a researcher through experiments, surveys, or observations for the specific purpose of the study. Secondary data, on the other hand, is information previously collected and processed by someone else, used by a researcher for a different purpose.